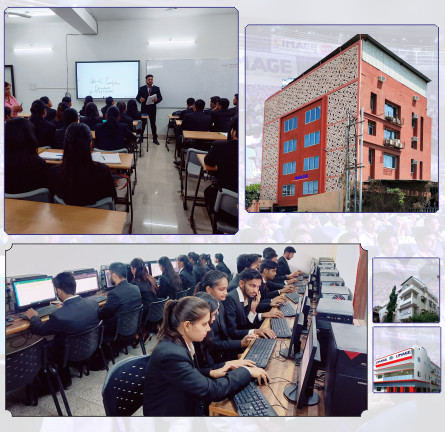
B.Sc. IT College in Patna | Get Admission for 2024-27 Session

Bachelor of Science in Information Technology B.Sc.(IT) is a Three Year Undergraduate Degree Course, which is divided into six semesters. A Bachelor of Science in Information Technology is a Bachelor’s degree awarded for an undergraduate course or program in the Information technology field. Being a best BSc IT college in Patna under Patliputra university, CIMAGE offers BSc IT course and campus placement in top multinational companies. Taking admission in BSc IT will be a good choice for the student as it is a job oriented course. CIMAGE college is the best choice to get admission for BSc.IT course as this college provides job opportunity along with the course.
The degree is normally required in order to work in the Information technology industry. This degree is primarily focused on subjects such as software, databases, and networking. This degree is awarded for completing a program of study in the field of software development, software testing, software engineering, web design, databases, programming, computer networking and computer systems. After the admission in BSc IT course, students will study about Computer and Information Technology related subjects in depth.
Bachelor of Science in Information Technology [B.Sc.(IT)]
- Duration : 3 Years
- Eligibility : +2 or Intermediate
- Course Duration : 3 Years (6 Semesters)
Why B.Sc. (IT) ?
In this Hi tech age of computers, where everything being digitalized, knowledge about The growth of IT industry is magnificent and evident. The Information Technology Industry is growing at a rapid pace. With the advent of globalization computers grew in prominence. computer and Information technology is very important. It helps the student have a distinct advantage over the others, who do not have a degree in Computer Applications. B.SC.(IT) is a technical course. After completing 3 Year Degree Course, one can make his/her career in the field of Computer Applications as well as in the field of Software & Web Development. CIMAGE is one of the Best BSc IT College in Patna to get admission as it is offering job placement after the course completion.
It’s a very good course but only for those who have interest in computer and want to see them as an IT Professional in future. If you are interested in Computer Science & Technical field, then B.SC.(IT) is the perfect course for you will get high package job in campus placement of CIMAGE college.
Skills to be learnt during B.SC.(IT)
Students who opt for a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology , B.SC.(IT) gets to learn programming languages such as Java, C++, HML, SQL, etc. Information about various computer applications and latest developments in IT and communication systems is also provided. Learners not only gets skills and information about Computer and Information Technology but also in communication, organization and Management too. You need to make a good choice for the admission in BSc.IT course.
Career opportunities after B.SC.(IT)
Once you get admission and completed this course from best BSc IT college in patna there are many opportunities available for you. Bachelor of Science in Information Technology (B.SC.(IT)) gives a number of opportunities to individuals to go ahead and shine in their lives. The range of chances in Information Technology (IT) are immense. Some are creative while others are highly technical. A few of them being like Software Programmer, System and Network Administrator, Web Designer, Software Programmer, Database Administration, Faculty for Computer Science/Communication Technology, etc. CIMAGE group is one of the finest college under PPU ( Patliputra university ) where students can get admission through entrance test or in some cases direct admission in allowed.
Future scope after B.SC.(IT)
Successful completion of Bachelor of Science in Information Technology (B.SC.(IT)) course from CIMAGE College gives an added advantage and builds a firm platform for IT professional. After completing the course, from Best BSc IT college in Patna students can start their career as programmers and rise to that of senior programmers. They can begin their career in IT industry as Junior Programmer and can get promoted as senior project managers and senior programmers. The ones, who works in some organization for a few years and then can go for their Masters in Computer Applications(MCA). After completing their masters one becomes specialized in that particular field. It gives a distinct advantage to the students in the field of Information Technology. Students who has completed their BSc IT course from CIMAGE college are getting job placement in top MNC companies.
One can land up either with a job or can think of starting up an IT business, as per their desire and interest that one always wished for or had an eye on. After the admission in CIMAGE college, students will be able to get a strong academic base with the help of which they can get advanced career in computer application by doing the B.SC.(IT) course in patna. B.SC.(IT) degree from CIMAGE college helps the students to get a sound knowledge on computer applications with the help of which they can have a perfect launch pad for challenging career in the field of information technology. Admission in CIMAGE college for this course is highly recommended for candidates willing to make it big in the field of information technology and related streams.
Industry Oriented Add-On Courses with a B.Sc (IT) Programme
Being a best B.Sc (IT) College in Patna it offers several latest Add-On Courses, as per the requirements of the Industry, which keeps students ready to meet the Global Challenges in the field of Information Technology, resulting in giving an edge to the CIMAGEians over the rest B.Sc (IT) Graduates.
-
MCA Entrance Preparation
-
Advance Web development Package
-
Advance Java Package
-
Computer Hardware & Networking
-
MCSE & CCNA
-
Training and Workshop on Digital marketing
-
Robotics
-
Linux and Open Office
-
Cloud Computing
-
Ethical Hacking
-
Mobile App, Web and Software Development
-
Advance Excel and PowerPoint
Why to Choose CIMAGE?
Fee Structure
| Course | Duration | Affiliation | Total Fee |
| BBM (PPU) | 3 Years | Patliputra University | ₹1,79,000 |
| B.Sc. (IT) (PPU) | 3 Years | Patliputra University | ₹1,79,000 |
| BCA (PPU) | 3 Years | Patliputra University | ₹2,11,000 |
| B.Com (P), (AKU) | 3 Years | Aryabhatta Knowledge University | ₹1,31,000 |
| BBA (AKU) | 3 Years | Aryabhatta Knowledge University | ₹2,11,000 |
| BCA (AKU) | 3 Years | Aryabhatta Knowledge University | ₹2,11,000 |
| PGDM (AIMA) | 2 Years | AIMA (All India Management Association) | ₹1,78,000 |
– Internal Examination Fee (Per Semester): ₹1000/-
– Library Security Deposit (Refundable): ₹1000/-
The above Fee Structure would be offered under the Down Payment Mode (option 1) Contact: 9835024444, 7250767676
Frequently Asked Question
A Bachelor of Science in Information Technology, (BSc-IT, is a bachelor’s degree or Undergraduate programme in information technology. The degree is normally required in the Information technology industry.
The Scope of BSc – IT is in the following areas:
Programming languages such as C, C++, Java, Python, etc.
Database management systems
Networking and security
Web development
Mobile app development
Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning
Cloud computing
BSc-IT is an ideal choice for those who have a flair for technology and would like to pursue it as a career. Many job opportunities are available in the field of IT, including:
- Software developer
- System administrator
- Network engineer
- Database administrator
- Web developer
- Mobile app developer
- Cloud engineer
- Cybersecurity analyst
The candidate must have studied physics chemistry and mathematics as compulsory subjects in their 10 + 2 class level. Without a mathematics subject, the candidate cannot apply for an information technology course.
A minimum of 50-60% in 10+2 with science background (Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics) or equivalentClear an entrance examination conducted by the college or university
Meet any other specific requirements set by the institution offering the program.
Additionally, students with a strong background in mathematics, physics, and other sciences, may be well-suited for this program.
- MCA Entrance Preparation
- Advance Web Development Package
- Advance Java Package
- Computer Hardware & Networking
- MCSC & CCNA
- Training and Workshop on Digital Marketing
- Robotics
- Linux and Open Office
- Cloud Computing
- Ethical Hacking
- Mobile App, Web, and Software Development
- Advance Excel and PowerPoint
CIMAGE Group of Institutions is one of Bihar’s best and No. 1 colleges. CIMAGE college provides the best placement facilities for BSc-IT courses in Patna, Bihar.
It depends on the specific government job you are interested in. Different jobs may require different educational backgrounds. For example, jobs in finance or economics may require a degree in those subjects, while jobs in science or technology may require a degree in those fields. It is important to research the specific requirements for the government jobs you are interested in and pursue a BSc in a relevant field. Additionally, having a good GPA, experience, and relevant skills could also help. Some of the best SSC CGL, RRB Entrance Exam, IBPS PO, SBI PO, etc.
Accenture is the No.1 IT Company in the world followed by TCS, Infosys, IBM Consulting, Capgemini, NTT Data, Cognizant, etc. Many students of the CIMAGE Group of Institutions are placed in such companies and now with time holding great positions as well.
Yes, a BSc-IT student can apply for and potentially get a job at Google. However, there is no guarantee of employment as the hiring process at Google is highly competitive and based on qualifications and experience. It is important for the student to have relevant skills and experience and to demonstrate their abilities through their resume, cover letter, and interviews.
Both BSc-IT and B.Tech are undergraduate degrees that provide students with a strong foundation in a specific field of study. The choice between the two depends on the student’s interests and career goals.
A BSc degree is typically a general degree in science, which covers a broad range of subjects and provides students with a broad understanding of the field. It is usually offered in fields such as biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics.
A BTech degree is a professional degree in technology, which focuses on a specific field such as computer science, mechanical engineering, or electrical engineering. It provides students with specialized knowledge and skills in their chosen field and prepares them for a career in a specific industry.
Both degrees have their advantages, it depends on the student’s field of interest and career goals. A BSc degree may be more suitable for students who want to pursue further studies in a specific field, while a BTech degree may be more suitable for students who want to enter the workforce immediately after graduation.
Yes, it is possible to get a job after completing a BSc-IT Computer Science. The field of computer science is a rapidly growing industry with a high demand for professionals with strong technical skills and knowledge. Graduates with a BSc in Computer Science have a wide range of career opportunities available to them, including software development, data analysis, and network administration.
Some of the popular job roles for BSc computer science graduates include:
- Software Developer
- System Analyst
- IT Consultant
- Data Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Network Administrator
- Technical Support Engineer
- Quality Assurance Engineer
A BSc-IT degree is a good option after 12th grade for students who are interested in pursuing a career in science or technology. The BSc-IT program provides students with a strong foundation in a specific field of study and prepares them for a wide range of career opportunities.
A BSc-IT program typically covers subjects such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology, and the student can choose to specialize in a specific field such as computer science, biotechnology, or environmental science. It is worth noting that the job prospects and salary of a BSc-IT graduate may vary depending on the field of specialization, the region, and the level of experience. It is highly recommended to research different fields and job opportunities before making a decision.
Some of the highest salary paying jobs after the 12th are: –
- BBA
- BSc-IT
- Bachelor in Computer Application.
- Bachelor of Science in Hotel Management.
- BBM
- B.COM
- LLB
Some of the best jobs for BSc-IT courses students are: –
- Software Developer.
- Software Engineer.
- Software Architect and
- Software Consultant
- Application Programmer.
- Database Administrator.
- Hardware and Network Expert.
- Computer Information Specialist.
- Enterprise Information.
- Officer Information.
- Systems Manager.
- Computer Support Specialist.
A BSc-IT can be a good choice for a career in the technology industry, as it provides a strong foundation in computer science and information technology. Graduates with a BSc in IT can pursue a variety of roles in fields such as software development, network administration, information security, and data analysis. As the technology industry is constantly evolving, the demand for IT professionals is expected to remain strong in the future. However, it is important to note that one’s future success will also depend on factors such as skills, experience, and ability to adapt to changing technologies. At CIMAGE Group of Institutions, thousands of students got campus placement in companies like Accenture, WIPRO, TCS, etc.
Yes!! Because in the BSc-IT curriculum, there is some programming language is also there. To do programming and practice programming, you need a laptop. The programming language that is present in the IT BSc-IT curriculum is C, C++, MySQL, and many more.
Yes, Coding is taught in both theory and practical format in BSc-IT. Skills like python, C++, C, etc are being taught in BSc-IT course.
BSc-IT typically includes courses that cover programming languages such as C, C++, Java, Python, and SQL. Other languages such as ja
CIMAGE Group of Institutions is the best college for BSc-IT courses in Patna, Bihar. CIMAGE College provides quality education, add-ons, & campus placement facilities.
Many universities and colleges offer placement or internship opportunities to their BSc students as a part of their curriculum. These opportunities can provide students with valuable work experience and help them develop the skills and connections needed to secure a job after graduation. CIMAGE Group of Institutions has dedicated placement cells that work with companies to arrange student internships and job opportunities.
Yes, Amazon does recruit BSc students for various roles. Amazon is a large and diverse company that offers a wide range of job opportunities in fields such as software development, operations, supply chain management, and data analysis. They also have various entry-level positions that are open to candidates with a BSc degree in relevant fields such as Computer Science, Information Technology, Mathematics, Physics, and related fields.
Yes, BSc students can join Infosys for various roles. Infosys is a large and diverse company that offers a wide range of job opportunities in fields such as software development, consulting, data analysis, and more. They recruit students from a variety of educational backgrounds and BSc students with relevant technical degrees such as Computer Science, Information Technology, Mathematics, Physics, and related fields are also eligible to apply. Students of CIMAGE got campus placement in companies like Infosys, Wipro, TCS, and Cognizant every year.
No, a bachelor’s in information technology is a 4-year programme for which entry is through a national entrance exam. It is a 3-year undergraduate programme with an emphasis on networking and software.
B.Sc (IT) Course Detailed Syllabus
(FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY)
UNIT – 1 (HARDWARE)
- Brief History of the development of Computers.
- Computer System Concepts: Features & Limitations.
- Basic components of Computer Hardware, CPU, Memory Unit & I/O Unit.
- CPU Organization – CU, ALU, Registers.
- Memory organization – RAM, ROM, EPROM, PROM, Cache Memory.
- I/O Organization – VDU, Keyboard, Mouse, and secondary I/O Devices.
- Mass Storage Organisation – Magnetic Tape, Magnetic Disk, CD, DVD, Flash Storage Devices.
- Data Representation – Number systems – Binary, Decimal, Octal. 2’s Complement. ASCII & EBCDIC Codes.
UNIT –II (INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE)
- Types of Software
- System Software
– Operating Systems
– Command interpreters
– Translator – Assemblers, Compilers, Interpreters.
- Types of Operating Systems
– Batch Processing
– Single Process Monitors
– Multiprogramming – Real-time
– Online
– Multiprocessing
- Programming Languages
– Machine Language
– Assembly Language
– High-Level Language
- Application packages
– Word Processors
– Spread Sheet
– Presentations
– Other Utilities
- Computer viruses – Working & spread of viruses, Types, and Control of viruses
- Communication & Transmission
- Analog & Digital Signals
- Modulation – Demodulation (MODEM)
- Transmission Mode – Simplex, Half Duplex, Duplex
- Line Configuration – Point to Point – Multipoint
- Definition of computer networks
- Types – LAN, WAN & MAN
- Communication Protocols
REFERENCES
- COMPUTERS TODAY – BY S. K. Basandra, Galgotia Publication
- FUNDAMENTAL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY – by Alexis Leon & Mathews Leon, Vikas Publishing House, New Delhi
- COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS – by P. K. Sinha – BPB Publications
(STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING USING ‘C’ LANGUAGE)
UNIT – I (PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS)
- Programs & Program Development
- Flow Charts
- Pseudo Codes
- Programming Technique
– Structured Programming
– Top-down approach
– Bottom-up approach
– Object Oriented Programming
UNIT – II (‘C’ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE)
- Overview – History & Features
- Structure of a ‘C’ Programme
- Variables, ex
pressions, Identifiers, Keywords, Data types & Constants Operators – Arithmetical, Logical, relational, Conditional & Bitwise. - Operators Precedence & Associativity
- ‘C’ – I/O – Character Based & Formatted
- ‘C’ Control Statements
– Decision Control – If, If-else, nested If-else
– Loops / Iteration – while, do-while, for-loops
– Break / continue/go to statements
- Arrays – Single & Multi-Dimensional
- Strings
- Functions – Call by Value & Call by Reference
- Introduction to pointers
- Recursion § Structure & Unions
- C – Files
REFERENCE
- PROGRAMMING IN ‘C’ – by E. Balaguruswany, TMH Publications
- PROGRAMMING WITH ‘C’ – by Gottfried, Schamus Series, TMH Publications
- O’ LEVEL PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS 7 SYSTEMS – by V.K. Jain, BPB Publication
- ‘C’ COMPLETE REFERENCE – by Herbert C, TMH Publications
(INTRODUCTION TO IBM ARCHITECTURES)
- Microprocessors & Microprocessor Families
- Personal computers – IBM & Apple Series
- IBM PC Characteristics – PC / PCAT/ PCXT
- 8086 Architecture
- DMA Controller & Configuration
- YGA Controller
- Arithmetic Co-processor
- Clocks
REFERENCE
- IBM PC – by Peter Norton
- COMPUTER ORGANISATION & ARCHITECTURE – by William Stallings, TMH Publications
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
UNIT – I (DBMS BASICS)
- DBMS vs Files
- Organization of DBMS
- Three Views & Schemes of DBMS
- DOL, DML, Queries, SQL
- Types of DBMS – Relational, Hierarchical & Network
- R – R Diagrams
- Generalization, Specialisation, Aggregation
Unit – II (RDBMS)
- Relation – Definition, Functional Dependency Domain, Attributes, Tuples, Fields
- Keys – Candidate Key, Primary Key, Foreign Key
- Codd’s Rules
- Normalisation up to BCNF
- Example RDBMS – ORACLE (Practical Classes)
REFERENCES
- DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPT – by Korth & Siberschatz
- AN INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE SYSTEM – by Bipin Desai
- DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS – by Leon & Leon, Vikas Publications
- AN INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE SYSTEM – by C. J. Date.
Section – B (OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS)
UNIT – I (OS BASICS)
- Definition of OS
- Functions of OS
- Types of OS
UNITS – II (PROCESS MANAGEMENT)
- Process Definition
- PCB, Process States
- Scheduling – Algorithms & Types
- FCFS, SJF, Round Robin
- LTS, STS, MTS
- Primitive & Non-Primitive Scheduling
- Deadlocks – Avoidance, Detection & Recovery
- Interprocess Synchronisation – Semaphores & Mutual exclusion
Unit – III (MEMORY MANAGEMENT)
- Fixed & Dynamic Partitions
- Compaction
- Paging
- Segmentation
- Virtual memory, Page Replacement Algorithms
UNIT – IV (DEVICE MANAGEMENT)
- Overview – Types of I/O – Serial & Block I/O
- Programmed I/O
- Interrupt Driven I/O
- DMA
- Polling, Daisy-Chaining, Multiple Interrupt Lines
- Device Drivers & Device Controllers, BIOS, IS<Device Independent Software
UNIT – V (FILE MANAGEMENT)
- Blocks, Sectors. Clusters, Directories
- Files – Concepts & Definitions
- Types of files & Organisations
- Disk Free Space Management
- Disk Free Space Allocation
- Disk Scheduling
UNIT – VI (DISK OPERATING SYSTEM (DOS)
- History & Versions
- Booting – FAT, Directory Structure
- DOS System Files
- DOS Commands – Internal & External
- DOS – Batch Files REFERENCE
- OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPT – by Galwin Stlberschatz
- OPERATING SYSTEMS – by Tanenbaum
- OPERATING SYSTEMS – by Dietel
BASIC ELECTRONICS – I
UNIT – I
- Types of resistance, Resistance symbol, Colour code, capacitor’s symbol, Code types, Mica & paper capacitor. Inductance, Conductor, Insulator, Band Theory, Intrinsic & extrinsic semiconductors, Theory of p-n Junction, Capacitance and diffusion capacitance
Unit – II
- Zener diode, Tunnel diode, Varactor diode, Power diode, photodiode, LED, LCD, Point contact. Diode. Schottky diode, Halfwave & full wave rectifier with & without filter
UNIT – III
- BJT characteristics, CE, CB, CC configurations, FET Metal oxide, Semiconductors (MOSFET). CMOS, Unijunction transistor & Phototransistor.
UNIT – IV
- Single stage RC coupled amplifier frequency response class A, Class B, Class AB, Class C, Push-pull amplifier, Efficiency distortion in amplifier their merits & demerits. BJT & FET RC coupled amplifiers.
UNIT – V
- Switching Characteristic BJT & FET, Monostable & Astable Multivibrators, RC integrators & differentiators, Clipper & Clamber circuit. REFERENCE
- BASIC ELECTRONICS – by B. L. Thareja
- BASIC ELECTRONICS – by A. K. Sahani
- BASIC ELECTRONICS – by V. K. Mehta
DATA STRUCTURE
- Dynamic Memory Allocation – Malloc (), Alloc ().]
- Analysis of Algorithms.
- Arrays – Searching, Sorting, Insertion, Deletion, Merging.
- String, Manipulation.
- Linked Lists – Single & Double, Operations.
- Sparse Matrices, Operations. Stacks – Operations, Infix, Prefix & Postfix Notations.
- Queues – Operations, Circular &Deque.
- Trees – BS Tree, AVL- Tree, B-Tree, Heap Searching & Sorting Techniques.
- Graphs – Adjacency, DFS BFS, Minimum Spanning Tree, Dijkstra & Kruskal Algorithms.
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
Unit – I Boolean Algebra
- Introduction to Boolean Algebra
- Basic Postulates
- Canonical Forms – Sum of Products & Product of Sums.
- Karnauge Maps
- Simplification Using Karnaugh Maps.
Unit – II Circuit Design
- Introduction to Digital Logic
- Gates – Invertors, AND, OR, XOR, UNIVERSAL NAND GATE, UNIVERSAL NOR GATE, TRUTH TABLES, AND LOGICS DIAGRAMS.
- Basic circuits – Adders, Decoders, Encoder, Multiplexers, Flip-Flops, etc.
UNIT – I / LINUX
- Basic Features, Advantages, Basic, Architecture of Unix / Linux System, Kernel, Shell.
- Linux File System – Boot Block, Super Block, Anode Table, Data Blocks, How Linux access files, storage files, Linux standard, directories, Commands for files and directories cd, Is, Cp, MD, RM, MKDIR, RMDIR, more, less, creating and viewing files, using cat, checking disk free spaces, Linux system start-up and shut-down process.
UNIT – II / LINUX
§ Understanding shells, Processes in Linux, connecting processes with pipes, redirecting input, and output, Background processing, managing multiple processes, changing process priority, scheduling of processing at command, batch commands, kill, PS, who, sleep, Printing commands, find, sort, Cal, Banner, touch, file, file related commands-was, sat, cut, grep, dd, etc, Mathematical Commands BC, EXPR, factor, units.
OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING CC++
Unit – I Oops Basics
- Objects
- Classes
- Polymorphism
- Reusability
- Inheritance
- Message
- Passing
- Genericity
Unit – II C++ Programming Language
- History & Features, Introduction of Classes, Compassion / Additional Features to C-Language.
- Object-oriented features in C++
- Scope Resolution Operator
- Static Data Member
- Static Function
- The passing object of function
- Returning Objects.
- Constructors & Destructors
- Function Overloading in C++, Operator Overloading in C++
- Inline Function, Friend Function
- Inheritance – Single, Multiple, Multilevel Virtual Functions
- Void Pointers
- Pure Virtual Functions
- Function Templets & Class Templets.
COMPUTER NETWORKING & INTERNET
UNIT – I
- Need & Advantages of Networks, Types: Server-based, Peer-Based, Hybrid.
- Topology, Network media types, H/w protocol, Software protocol, digital signalling, analogue signalling, bit synchronization, baseband, and broadband transmission.
Unit – II
- OSI and IEEE 802 Model, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.4 IEEE 802.5 & fast Ethernet FDDI, A TM, LAN access techniques, Bit map protocol.
Unit – III
- Connectivity, Hubs, Repeaters, Bridges, Multiplexers, Router, Gateways, Modem, Types of Modems, Modulation Schemes.
Unit – IV
- Internet V/s Intranet, growth, ISP, Connectivity, Dial-up, leased line, URL, Domain name Portals Application, POP & Web-based e-mail, merits, IP addressing.
- Basics of sending &receiving e-Mails.
Unit – V
- Internet Chatting, WWW, HTTP, URL, HTML.
- Overview of e-commerce, Internet, e-business, and Advantage of E-commerce.
DIGITAL COMPUTER ORGANISATION
Unit – I
- CUP ORGANIZATION: ALU & Control Circuit, Idea about Arithmetic, Circuits, Program Control, Instruction Sequencing.
Unit – II
- INPUT-OUTPUTORAGANIZATIONS: I/O interface, Properties of simple I/O devices and their controller, Isolated Versus memory-mapped, I/O, Modes of Data transfer, Synchronous & Asynchronous Data transfer, Handshaking, Asynchronous serial transfer, I/O Processor.
Unit –III
- MEMORY ORGANIZATION: Memory Hierarchy, Auxiliary memory, Magnetic drum, Disk & Tape, Semi-conductor, memories, Associative, memory, virtual Memory, Address Space & Memory space, Address mapping, Pages table, Page Replacement, Cache memory, Hit Ratio, Various mapping techniques, writing into Cache.
JAVA PROGRAMMING
Unit – I
- C++ Vs Java, Java and Internet, and WWW, Java support systems, Java environment, Java Program Structure, Tokens, Statements, Java Virtual machine, ex
pressions & its Evaluation, Data Types, Jumps in Loops, Labelled Loops.
Unit – II
- Defining a class, adding variables and methods, creating objects, assessing class members, Constructors, Method overloading, Static members, Nesting of methods, Inheritance: Extending a class, Overriding methods, Final variables and methods, Final classes, Finalizer methods, Abstract methods and classes, Visibility control.
Unit – III
- Arrays, one dimensional & two-dimensional Strings, Vectors, Wrapper classes, and Defining interfaces. Extending interfaces, implementing interfaces, accessing interface Variables, System packages, Using System packages, Naming Conventions, -creating packages, accessing packages Using packages, Adding a class to a package, Hiding classes.
Unit – IV
- Threads, creating threads, Extending the threads class, Stopping and blocking a thread, Life cycle of a thread, using thread methods, Thread exceptions, Thread priority, Synchronization, and Implementing the runnable interface.
Unit – V
- Applets, Local and remote applets, Applets Vs applications, Writing applets, Applets life Cycle, Creating an executable applet, Designing a web page, Applet age, Adding applet to HTML file, Running the applet, Passing parameters to applets, Aligning the display, HTML tags &applets, Getting input from the user.
Internet and Web Designing
Unit – I
- Introduction to internet Applications: Introduction to the internet, WWW, Newsgroup, E-Mail, Messaging Protocols, Inter Protocols (HTTP, FTP, TFTP, DNS, SMTP, IMAP, POP, and TCP/IP), Setting up an Internet connection using Dial-up and leased-line (broadband). Creating e-mails, sending emails, and Attachments, using FTP services.
Unit –II
- Web Page Designing: using different browsers. (Internet Explorer / Netscape Navigator) Browsing internet and E-mail service providers, features of internet Services (Chatting, Conferencing), MIRC, HTML &DHTML: HTML tags, Designing Tables, Frames, and Forms, placing images, animation, and Sound on Sites, Using Hit Counter. Adding VB Script code HTML pages, Scripting Functions. Using Front Pages 2002 Hosting your website using Free hosting Sites like yahoo, Angel fire, etc.
Unit – III
- Server-side programming using ASP: Asp objects, DOM, Database accessing on Web, using forms to perform Query in Database.
SECTION – C INTRODUCTION TO NETWORK SECURITY
Unit – I
- Introduction: Networking Terminologies, Active Vs Passive Attacks, Viruses, Worms, Trojan Horse. The Multi-Level Model of Security, Legal Issues. Introduction, Breaking an Encryption Scheme, Types of Cryptographic Functions-Secured Key, Public Key, and Hash Algorithms. Data Encryption Standards, International Data. Encryption algorithm, Advanced Encryption Standard, RC4 Modes of Operation, encrypting a large message, Generating MACs, Multiple Encryption DES. Public Key Algorithm, Modular Arithmetic, RSA, Diffie-Hellman, Digital Signature Standard.
Unit – II
- Authentication: Password-based, Address based, cryptographic authentication protocols, Eavesdropping and Server Database reading, Trusted Intermediaries, Session Key, Authentication of people Security Handshake pitfalls. Electronic Mail Security, PGP (Pretty GOOD Privacy). Firewalls, web Issues.
VISUAL PROGRAMMING WITH VISUAL BASIC
Unit – I
- Visual Programming: The fundamentals of Visual Basic, Introduction, VB Editions, working with visual Basic, IDE, the element of the user interface, Designing the user Interface, Programming an application, Visual Development, Event-Driven Programming, Customizing the environment.
- Visual Basic the Language: Visual basic projects, the project files, variables, constants, Arrays, Collections, procedures, arguments, the function returns values, control flow statements, looping statements, nested control structures, and exit statements.
- Working with forms: The appearance of the form, designing menus, building dynamic forms, drag and drop operations, and mouse conflicts.
- Basic Active X Controls: The textbox control, the list box, and combo box controls, the scroll bar and slider controls, and the file controls.
- Advanced Active X Controls: The common dialogs control, using the common dialog control the tree view and list controls, the rich text box control, the RTF languages, and the Ms flex grid control.
- Multiple Document Interface: MDI applications, parent and child and child MDI forms Accessing child forms, Implementing scrolling forms.
- Database Programming with VB: The Active data objects, data environment, SQL, Ms flex grid control, ado, Dao, Library, Report designing using data report. Interfacing with MS-access & Oracle database.
SYSTEM ANALYSIS & DESIGN
Unit – I
- SYSTEM CONCEPTS: The system concept, Characteristics of system, Elements of system, Types of system, man-made information systems.
- SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE: Recognition of need, Feasibility Study, Analysis, Design implementation, post-implementation, and maintenance System planning and control.
- SYSTEMS PLANNING AND INITIAL INVESTIGATION: Bases for Planning system analysis, Determining user’s requirements and analysis, Fact-finding, and Determination of feasibility.
- TOOLS OF STRUCTURED ANALYSIS: Logical and Physical Models, Data flow diagram, Data dictionary, System structured charts, System model, Pseudo codes, Decision tree, Decision tables, HIPO chart, Gantt charts, Worries diagram.
- FEASIBILITY STUDY: System performance constraints, identification of system objective, feasibility analysis, and report.
- SYSTEM DESIGN: Stages of system design, Logical and Physical design methods, From driven mythologies; IPO and HIPO charts, structured walk-through, Audit considerations; Processing controls, Data validation, Audit trail, and documentation control
SQL SERVER
Unit – I
- Introduction: SQL Server 2000 Relational Database Management System and Conventional database systems. Installing SQL Server. Working with Enterprises Manager. Configuring a Database, Creating Tables, Views, defining constraints, and Creating relationships. Designing Database diagram. Creating Indexes. Creating user-defined data types, Creating Stored Procedures and Functions.
- Working with Query Analyzer, writing queries, using relational operators like a project, join, Intersect, union, and difference. Built-in SQL functions. Performing data manipulation from query analyser. Query optimization.
- Using OLE DB, and ADO for interfacing with front-end application designs in VB, Java, etc.